Traffic Management
This workshop has been deprecated and archived. The new Amazon EKS Workshop is now available at www.eksworkshop.com.
Create the default destination rules
Deploying a microservice-based application in an Istio service mesh allows one to externally control service monitoring and tracing, request (version) routing, resiliency testing, security and policy enforcement, and more in a consistent manner across the services, and the application.
Before you can use Istio to control the Bookinfo version routing, you’ll need to define the available versions, called subsets.
In a continuous deployment scenario, for a given service, there can be distinct subsets of instances running different variants of the application binary. These variants are not necessarily different API versions. They could be iterative changes to the same service, deployed in different environments (prod, staging, dev, etc.). Common scenarios where this occurs include A/B testing, canary rollouts, etc. The choice of a particular version can be decided based on various criterion (headers, url, etc.) and/or by weights assigned to each version. Each service has a default version consisting of all its instances.
kubectl -n bookinfo apply \
-f ${HOME}/environment/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml
We can display the destination rules with the following command.
kubectl -n bookinfo get destinationrules -o yaml
Route traffic to one version of a service
To route to one version only, we apply virtual services that set the default version for the microservices. In this case, the virtual services will route all traffic to reviews:v1 of the microservice.
kubectl -n bookinfo \
apply -f ${HOME}/environment/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-all-v1.yaml
We can display the review virtual service with the following command.
kubectl -n bookinfo get virtualservices reviews -o yaml
The subset is set to v1 for all reviews request.
Try now to reload the page multiple times, and note how only version 1 of reviews is displayed each time.
Route based on user identity
Next, we’ll change the route configuration so that all traffic from a specific user is routed to a specific service version.
In this case, all traffic from a user named Jason will be routed to the service reviews:v2.
kubectl -n bookinfo \
apply -f ${HOME}/environment/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-test-v2.yaml
We can display the updated virtual service with the following command.
kubectl -n bookinfo get virtualservices reviews -o yaml
The subset is set to v1 in default and route v2 if the logged user is match with ‘jason’ for reviews request.
To test:
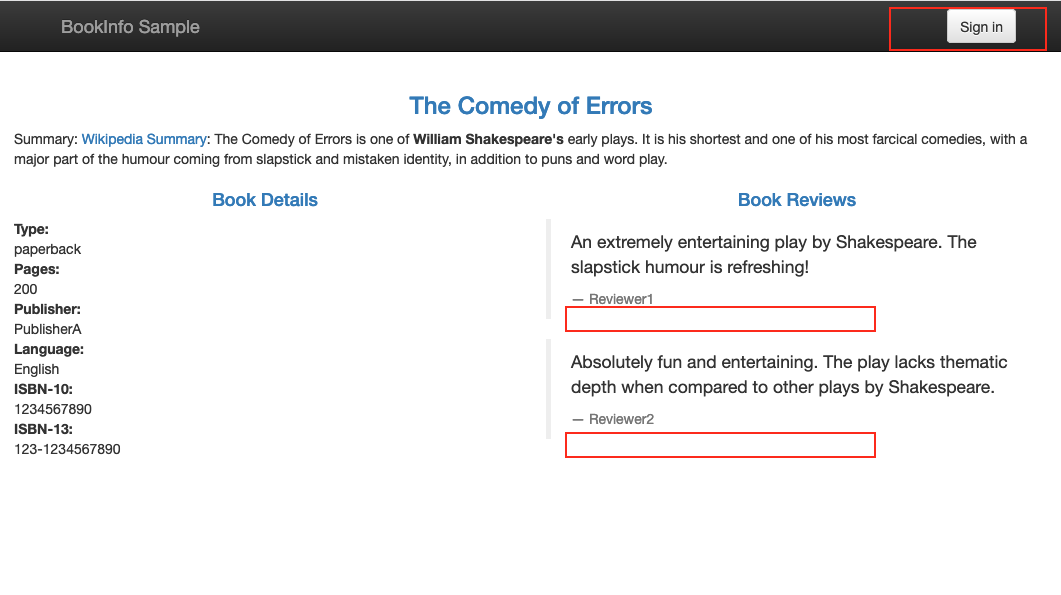
- Click Sign in from the top right corner of the page.
- Log in using jason as user name with a blank password.
You will only see reviews:v2 all the time. Others will see reviews:v1.
Injecting an HTTP delay fault
To test for resiliency, inject a 7s delay between the reviews:v2 and ratings microservices for user jason. This test will uncover a bug that was intentionally introduced into the Bookinfo app.
kubectl -n bookinfo \
apply -f ${HOME}/environment/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-ratings-test-delay.yaml
We can display the updated virtual service with the following command.
kubectl -n bookinfo get virtualservice ratings -o yaml
The subset is set to v1 in default and added 7s delay for all the request if the logged user is match with ‘jason’ for ratings.
Logout, then click Sign in from the top right corner of the page, using jason as the user name with a blank password. You will see the delays and it ends up display error for reviews. Others will see reviews without error.
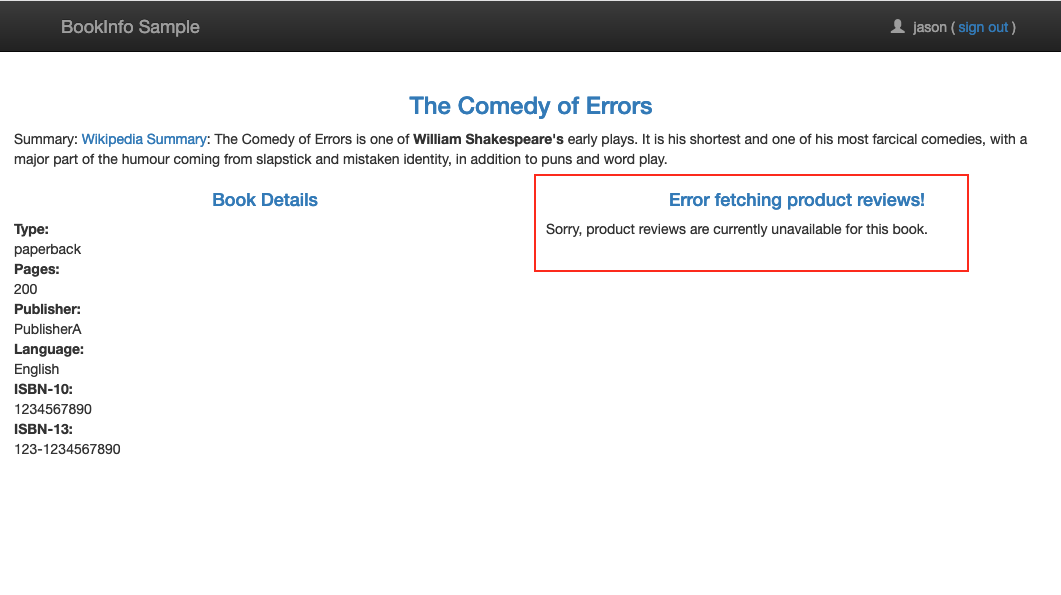
The timeout between the productpage and the reviews service is 6 seconds - coded as 3s + 1 retry for 6s total.
To test for another resiliency, we will introduce an HTTP abort to the ratings microservices for the test user jason. The page will immediately display the “Ratings service is currently unavailable”
kubectl -n bookinfo \
apply -f ${HOME}/environment/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-ratings-test-abort.yaml
We can display the updated virtual service with the following command.
kubectl -n bookinfo get virtualservice ratings -o yaml
The subset is set to v1 and by default returns an error message of “Ratings service is currently unavailable” below the reviewer name if the logged username matches ‘jason’.
To test, click Sign in from the top right corner of the page and login using jason for the user name with a blank password. As jason you will see the error message.
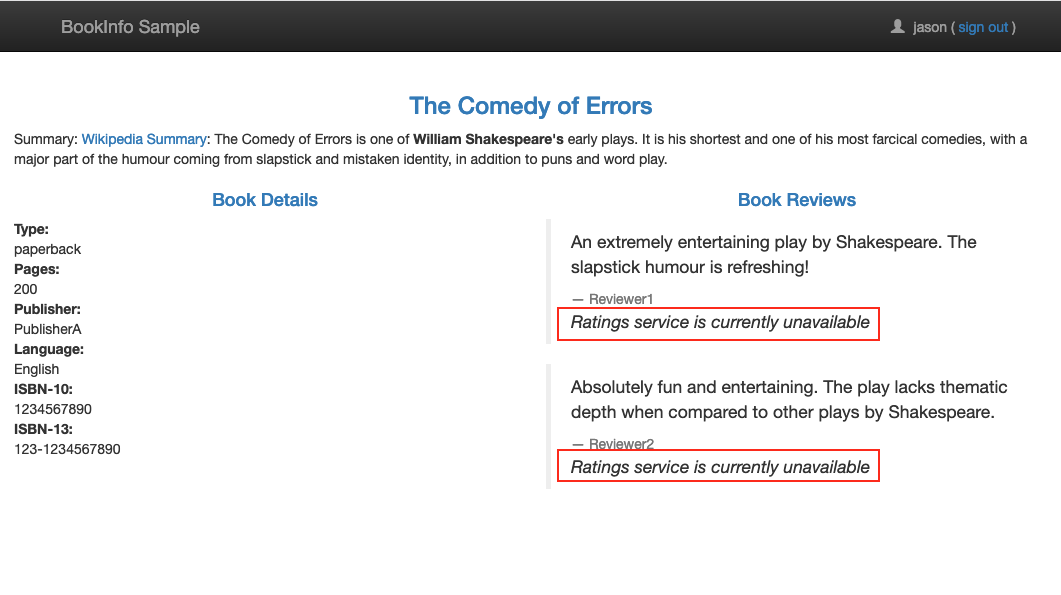
Others (not logged in as jason) will see no error message.
Traffic Shifting
Next, we’ll demonstrate how to gradually migrate traffic from one version of a microservice to another. In our example, we’ll send 50% of traffic to reviews:v1 and 50% to reviews:v3.
To get started, run this command to route all traffic to the v1 version of each microservice.
kubectl -n bookinfo \
apply -f ${HOME}/environment/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-all-v1.yaml
Open the Bookinfo site in your browser. Notice that the reviews part of the page displays with no rating stars, no matter how many times you refresh.
We can now transfer 50% of the traffic from reviews:v1 to reviews:v3
kubectl -n bookinfo \
apply -f ${HOME}/environment/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-50-v3.yaml
kubectl -n bookinfo get virtualservice reviews -o yaml
The subset is set to 50% of traffic to v1 and 50% of traffic to v3 for all reviews request.
To test it, refresh your browser over and over, and you’ll see only reviews:v1 and reviews:v3.
Assuming you decide that the reviews:v3 microservice is stable, you can route 100% of the traffic to it
kubectl -n bookinfo apply -f ${HOME}/environment/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-v3.yaml
Now when you refresh the /productpage you will always see reviews:v3 (red colored star ratings).